Smart Government Initiatives: How Governments are driving digital change
Digital Changes and Transformation in Government
The transformation or changes in relation to the digital innovation indicates the replacement of the traditional and legacy application and manual processes by using new technologies throughout the organisational operations (Tangi et al. 2021). This is generally done for improving the effectiveness, efficiency, service delivery as well as customer experience in all the public sector at different times. In relation to the government sector, the digital transformation consists of using new technologies through which public services can be improved, so that better customer and business experiences can be created with the government offices. In accordance with this discussion it can be stated that the key objective of digital transformation or changes is establish more transparent, efficient as well as responsive public sector through which all the needs of the public can be accomplished (Clarke, 2020).
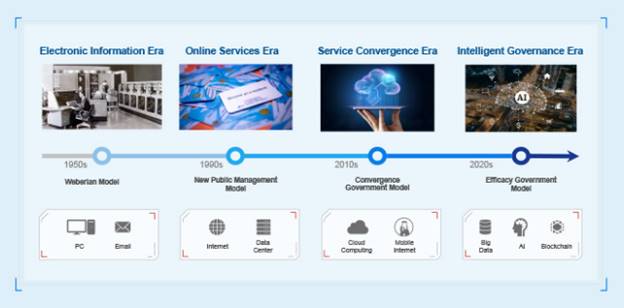
Figure 1: Intelligent Governance in Digital Governments
(Source: huawei.com, 2024)
Thus through this change it can be understood that the public sector or government offices can operate using the changes in the technology to streamline processes. In this way the data management can be improved for creating the better experiences for the citizens. Digital transformation or changes within the government can take place in several forms which also consists of replacement of the outdated systems, development of the modern digital environment as well as considering the automation as well as artificial intelligence (Pittaway and Montazemi, 2020). In this way, the overall service delivery can be improved and operational costs can be reduced.
Graduation from UK , Post Graduation from United Kingdom , student help in United Kingdom
Factors Driving Digital Transformation in Government
Since the 1900s, Different countries across the globe have faced different types of changes in the context of political, economic, social, and cultural environment. Throughout these changes, governments of different countries have encountered several complicated as well as unpredictable global scene where the uncertainties have been continuously increased along with a rapidly evolving international setting, as well as social and economic conflicts (Castro and Lopes, 2022). Therefore in relation to this, these increasing need for satisfactory public service experiences have been made it vital for governments a focus on being ‘people-cantered’ in the development of digital governance worldwide can get prioritised.
Based on the above discussion, it can be stated that for the economic development as well as government modernisation, within the government data has become a strategic and crucial asset as by utilising modern big data can overall modernise entire structure of the government. In this way the whole system can become more diversified as well as open (Chen et al. 2021). In accordance with this discussion, data, cyber security as well as privacy protection could become the key components of the national sovereignty. This is because in this way the government across different countries could digitally transformed and provide safe as well as reliable information network, data protection as well as application platform, so that, social, national as well as public information can be safeguarded.
Figure 2: New Dimension of Governance and Public Services
(Source: huawei.com, 2024)
According to different market researches, as the globalisation has taken place and industrial competition has been increased, most of the government across different countries have expanded their digital economy and quickly it has become a key driver of the GDP growth of those countries. These kinds of scenario therefore require governments to implement and provide proper guidance as well as governance at the strategic level (Van Veldhoven and Vanthienen, 2022). Thus, considering this discussion, it can be seen that there are several uncertainties which have led towards the increasing demand on the public services as well as social governance. Along with this, the modernisation process has been accelerated which has carried out several issues and a broader range of the social problems in the field of education, healthcare, environment protection as well as transportation and more.
Digital Government Transformation in Different Nations
There are different countries, especially the developed countries where the governments have taken several initiatives to adopt the digital transformation in this context (Kraus et al. 2021). In relation to this, in Australia, there has been a recent increase in strategic efforts as well as measures which can be focused on digitalisation as well as digital transformation. This has been therefore highlighted in 2015 by setting up the Digital Transformation Office. The primary objective in this context was to establish a unified digital identity system which can further allow the individuals to access different government services online through a single login process. Another example in this context could be UK, where a digital transformation initiative has been initiated, like the establishment of the Digital Transformation Office in Australia (Dąbrowska et al. 2022). In February 2016, the administration of UK has also been declared the creation of a new advisory committee which has further aimed to guide its digital transformation through which the development of its digital government services by enlisting the ‘digital experts’. This move has become an essential for the numerous analysts. Similarly, within the USA, “United States Digital Services” has been taken to transform the way through which the federal government can deal with their citizens. In this way, the access to the government information programs can be improved. Thus, in this regard, it can be found out that governments across different countries have made their investment in the digital initiatives to enhance the digital changes as well as transformation across the economy (Hai et al. 2021). In this regard, the example could be the Belgian Government who has been invested in data-sharing initiatives for fostering the transformation as well as innovation in public-private context.
Benefits of Digital Government Services
It can be stated that though there are some risks as well as challenges which have been faced by the government after choosing the digital governmental services, there are several benefits which can be founds out through digital transformation within the governmental sector, such as,
- By adopting different contemporary software, governments of different countries could switch from old-fashioned manual procedures to automated devices which can enable the staffs or employees of government to concentrate on several important tasks in this context (AlNuaimi et al. 2022)
- By adopting modern digital technology the employees are allowed to get more satisfaction with their works in every day’s life. In this way the repetitive services could be automated while digital transformation could help the government to maintain more effective collaborative tools (Vuksanović Herceg et al. 2020). This can easily enhance the relationship among the employees within the government sectors which can further create happier workplace
- By converting services that interact with citizens, like renewing licenses and permits, into digital formats, the enhancement of the effectiveness of the processes could be possible and also the utilisation of the services can be strengthened more
- Adopting contemporary digital applications within the government enterprises could decrease the dependency on the physical documents through which accessibility of the data can be enhanced (Alvarenga et al. 2020). Moreover, through digital transformation, government can get electronic records which can provide greater security compared to their paper or manual works. Therefore considering the encryption as well as access restrictions, the chances of data leaks or unauthorized entry could be lowered
- Digital change as well as transformation could enable the governments to collect all the additional information through which the demand and actions of the individuals can be comprehended (Kassen, 2022). As produced data can be abundant by using different online activities, public sector bodies can customer their services through which the requirements of their citizens can be fulfilled
- Though digital transformation can be costly still it can help the public or government entities o save money by using the automation processes. Furthermore, it can help the government entities to eliminate any kinds of costly mistakes which could be caused by the insufficient resources or lack of data sources (Llopis-Albert et al. 2021)
Challenges Faced by Government in Digital Transformational Context
Based on the above discussion, it can be stated that digital transformation can be considered as one of the inevitable steps for the government or public sectors of most of the countries (Matthess and Kunkel, 2020). But similarly this digital change could create several challenges as well which are as follows, such as,
- Sometimes digitisation of the systems could create risks by increasing the hacker attacks which further could destroy the confidentiality of the customers, different types of personal and crucial data as well as more
- On the other side, political unrest can negatively affect the digital transformation initiatives taken by the government. Sometimes political parties of different countries can resist the digital transformation initiatives as they can consider these digital changes as the threatening to the traditional governmental operations (ElMassah and Mohieldin, 2020). Some political group could resists to use the digital services due to the mistrust as well as stigmatisation
- By adopting the digitisation, government of different countries are required to adopt some steps which might be challenging for them like, reducing the manpower, closing some departments as well as reorganising the existing processes under different circumstances (Timotheou et al. 2023). These entire processes therefore could be time consuming and sometimes costly
Reference list
AlNuaimi, B.K., Singh, S.K., Ren, S., Budhwar, P. and Vorobyev, D., 2022. Mastering digital transformation: The nexus between leadership, agility, and digital strategy. Journal of Business Research, 145, pp.636-648.
Alvarenga, A., Matos, F., Godina, R. and CO Matias, J., 2020. Digital transformation and knowledge management in the public sector. Sustainability, 12(14), p.5824.
Castro, C. and Lopes, C., 2022. Digital government and sustainable development. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 13(2), pp.880-903.
Chen, C.L., Lin, Y.C., Chen, W.H., Chao, C.F. and Pandia, H., 2021. Role of government to enhance digital transformation in small service business. Sustainability, 13(3), p.1028.
Clarke, A., 2020. Digital government units: what are they, and what do they mean for digital era public management renewal?. International Public Management Journal, 23(3), pp.358-379.
Dąbrowska, J., Almpanopoulou, A., Brem, A., Chesbrough, H., Cucino, V., Di Minin, A., Giones, F., Hakala, H., Marullo, C., Mention, A.L. and Mortara, L., 2022. Digital transformation, for better or worse: a critical multi‐level research agenda. R&D Management, 52(5), pp.930-954.
ElMassah, S. and Mohieldin, M., 2020. Digital transformation and localizing the sustainable development goals (SDGs). Ecological Economics, 169, p.106490.
Hai, T.N., Van, Q.N. and Thi Tuyet, M.N., 2021. Digital transformation: Opportunities and challenges for leaders in the emerging countries in response to COVID-19 pandemic. Emerging Science Journal, 5(1), pp.21-36.
huawei.com, (2024), Accelerating the Digital Transformation of Government, Available at: https://e.huawei.com/es/ict-insights/global/ict_insights/ict31-digital-government/features/how-improving-digital-leadership-will-accelerate-the-digital-transformation-of-government [Accessed on 19.06.2024]
Kassen, M., 2022. Blockchain and e-government innovation: Automation of public information processes. Information Systems, 103, p.101862.
Kraus, S., Jones, P., Kailer, N., Weinmann, A., Chaparro-Banegas, N. and Roig-Tierno, N., 2021. Digital transformation: An overview of the current state of the art of research. Sage Open, 11(3), p.21582440211047576.
Llopis-Albert, C., Rubio, F. and Valero, F., 2021. Impact of digital transformation on the automotive industry. Technological forecasting and social change, 162, p.120343.
Matthess, M. and Kunkel, S., 2020. Structural change and digitalization in developing countries: Conceptually linking the two transformations. Technology in society, 63, p.101428.
Pittaway, J.J. and Montazemi, A.R., 2020. Know-how to lead digital transformation: The case of local governments. Government information quarterly, 37(4), p.101474.
Tangi, L., Janssen, M., Benedetti, M. and Noci, G., 2021. Digital government transformation: A structural equation modelling analysis of driving and impeding factors. International Journal of Information Management, 60, p.102356.
Timotheou, S., Miliou, O., Dimitriadis, Y., Sobrino, S.V., Giannoutsou, N., Cachia, R., Monés, A.M. and Ioannou, A., 2023. Impacts of digital technologies on education and factors influencing schools’ digital capacity and transformation: A literature review. Education and information technologies, 28(6), pp.6695-6726.
Van Veldhoven, Z. and Vanthienen, J., 2022. Digital transformation as an interaction-driven perspective between business, society, and technology. Electronic markets, 32(2), pp.629-644.
Vuksanović Herceg, I., Kuč, V., Mijušković, V.M. and Herceg, T., 2020. Challenges and driving forces for industry 4.0 implementation. Sustainability, 12(10), p.4208.
academhelper.com academhelper.com
"Looking for a Similar Assignment? Get Expert Help at an Amazing Discount!"