Explore the future of work with AI and its impact on employment trends
Artificial Intelligence (AI) at present is revolutionising the way of working as well as reshaping the landscapes of employment across the industries. Thus, with advancements of technology, they not only would be automating the routine tasks but would also be paving the path for completely new hob roles that would require creativity alongside complex nature of problem-solving and emotional intelligence. This specific transformation therefore often referred as the Industry 4.0 or Fourth Industrial Revolution, presenting opportunities and challenges both. In context of this exploration, the discussion would delve into the way AI is subject to redefine the place of working, emerging trends of employments and what organisations and engaged individuals can do for preparing for the future where skills of human and efficiency level of machine is coexisting.
In context of the present discussion, it can be stated that integration into the workplace is observed to be gradual yet highly profound. In the manufacturing process, robotics as well as machine learning is found to have enabled smart factories, where, automated systems are performing tasks that are repetitive in nature. That is also with higher level of precision alongside efficiencies compared to human workers (Gill et al. 2022). For example; automotive assembly lines at present employs arms that are robotics and can seamlessly assemble vehicles at speed that is unmatched by any human labour traditionally. Likewise; the industry of service has further seen increasing usage of chatbots and virtual assistance, which can handle inquiries of the target customers all the time. That holistically decreases the wait time and simultaneously support the processes.
Figure 1: AI Integration at Workplace
(Source: leewayhertz.com, 2025)
These advancements correspondently would not only improve level of productivity but would also be freeing up the human labours or workers for focusing on more tasks that are completely strategically led. However, on the other hand, it can be seen that they would also rise regarding the displaced jobs. In this context, it can be implied that job roles that are heavily relying on the repetitive tasks are being vulnerable in rising manner (Tschang and Almirall, 2021). Moreover, while some of the sectors are seen to be facing job losses potentially, others are equally being the witness of transformation that would be calling for blended technical expertise with human-driven knowledge and skills. That is also by setting the platform for the new trends of employment.
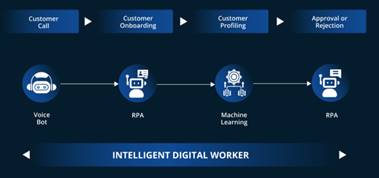
Following the discussion, it can be comprehended that regardless of tension revolving around automation process, AI integration is equally creating the myriad of scopes. Opportunities of new job roles like data scientists as well as AI ethics managers and engineers surrounding machine learning are emerging. That holistically has demanded unique blend of prowess technically and strategic rationalising and thinking (Morandini et al. 2023). For instance; it can be stated that multinational corporations like Google and Amazon both have expanded their teams to involve specialists who would not only establish the algorithms but would also be ensuring that these systems are adhering to the guidelines of ethical protocols and not propagating any sort of biases.
Figure 2: Impact of AI on Job Market
(Source: medium.com, 2025)
Moreover, it is also to be seen that gig economy alongside working remotely as the developing trends at present has received major boost from AI. Considerably, freelancers at present have core access towards advanced level of platforms digitally that can match their core skills with the needs of the project undertaken in the real-time context. These platforms as a result leverage AI for analysing trends of the market with capabilities on individual level (Malhotra, 2021). That is also by offering recommendations of personalised job prospects. Therefore, such developments would be empowering workers in crafting careers that might not be confined for traditional 9 to 5 framed jobs. That holistically as a result fosters highly fostering and adaptive market of labour.
It is further to be seen that while innovations being AI-driven has promised enhanced level of productivity and satisfaction for job, they would also come with challenges that are considerable. The displacement of traditional job roles is the fundamental concern, specifically for workers across the industries where automation would be prevalent mostly (Christiaensen et al. 2021). For instance; rise of autonomous vehicles can threat transportation disruptions and logistic sector potentially could see leaving of millions of drivers alongside related service workers without any employment.
This specific shift has certainly necessitated wider strategies to be adapted. Thus, contextually, companies should be investing in employee training programs that would focus on digital literacy and upskilling. That is also to ensure that the workforce to remain highly relevant. On the other hand, governments as well have crucial role for playing through facilitation of educational reformation and offering incentives for learning throughout the life (Zarifhonarvar, 2024). These measures therefore are pivotal in prevention of wider gaps in skills and ensuring that advancement in technologies can translate into growth inclusively compared to disparities socioeconomic contexts.
Contextually, it can be said that future of work in certain AI-driven world would be hinging on capabilities of adapting. Thus, in this context, reskilling initiatives would not merely be the remedy in short-term yet considered as strategy in long-term for equipping the workforce with essential skills for thriving in the competitive market. On the other hand, it is also to be considered that organisations that would be prioritising continuous learning most likely to outperform those that would not (Li, 2024).
Figure 3: Future of Employment Scope
(Source: pcma.org, 2025)
Therefore, corporate training programs and partnerships with educational organisations are emerging as core critical investments in this significance. These efforts further being combined with proactive set of mind towards technological transformation would ensure that advantages of AI are being shared widely throughout the society by mitigating risks related with automation rapidly.
Artificial Intelligence UK, dissertation writing help UK, essay writing help UK, write my dissertation
In conclusion, it can be implied that AI integration into the workplace would be offering opportunities unprecedentedly for the purpose of securing efficiencies and innovation, while also imposing risks for traditional structure of employment. Therefore, with embracing AI as the tool for enhancement instead of replacement, organisations as well as the workers likewise can navigate the transformative era at present. Moreover, emphasising on continual learning alongside adaptive strategies would be the core to harness potential of AI. That is also by ensuring that future of work is labelled by collaboration in between human ingenuity as well as artificial or machine intelligence. Henceforth, as a whole, it can be implied that success of that certain transformation is resting on the collective capability of innovation, adaptations and thriving in rapidly transforming world.
Christiaensen, L., Rutledge, Z. and Taylor, J.E., 2021. The future of work in agri-food. Food Policy, 99, p.101963.
Gill, S.S., Xu, M., Ottaviani, C., Patros, P., Bahsoon, R., Shaghaghi, A., Golec, M., Stankovski, V., Wu, H., Abraham, A. and Singh, M., 2022. AI for next generation computing: Emerging trends and future directions. Internet of Things, 19, p.100514.
leewayhertz.com, (2025), AI in business process automation: Use cases, benefits, technologies, implementation and development, Available at: https://www.leewayhertz.com/ai-in-business-process-automation/ [Accessed on 10.02.2025]
Li, L., 2024. Reskilling and upskilling the future-ready workforce for industry 4.0 and beyond. Information Systems Frontiers, 26(5), pp.1697-1712.
Malhotra, A., 2021. The postpandemic future of work. Journal of management, 47(5), pp.1091-1102.
medium.com, (2025), AI on the Job Market and Future of Work, Available at: https://medium.com/@Shahriare/ai-on-the-job-market-and-future-of-work-3e4615f8a443 [Accessed on 10.02.2025]
Morandini, S., Fraboni, F., De Angelis, M., Puzzo, G., Giusino, D. and Pietrantoni, L., 2023. The impact of artificial intelligence on workers’ skills: Upskilling and reskilling in organisations. Informing Science, 26, pp.39-68.
pcma.org, (2025), Future of Work: Impact of AI on the Workforce, Available at: https://www.pcma.org/pcmaapaclabs-june-series-recap-future-of-work/ [Accessed on 10.02.2025]
Tschang, F.T. and Almirall, E., 2021. Artificial intelligence as augmenting automation: Implications for employment. Academy of Management Perspectives, 35(4), pp.642-659.
Zarifhonarvar, A., 2024. Economics of chatgpt: A labor market view on the occupational impact of artificial intelligence. Journal of Electronic Business & Digital Economics, 3(2), pp.100-116.
academhelper.com academhelper.com
"Looking for a Similar Assignment? Get Expert Help at an Amazing Discount!"