Analyzing the impact of trade wars on the Global Economy
Trade wars defined by reciprocal rise in tariffs as well as non-tariff barriers among the countries have become common features increasingly considering international economic relations. Their core impacts are observed to be extended effectively beyond immediate tariff costs, which are also by affecting process of global supply chains, flows of investments and holistic stability in the economy. Thus, in this correspondence, the article at present is subject to analyse the multifaceted impacts of trade wars on the global economy. Moreover, by understanding these core dynamics, policymakers as well as business leaders would be able to navigate the complexities of global trade effectively in the era that is marked by economic nationalism alongside protectionism.
Trade wars are defined by governments in context of imposing quotas, tariffs as well as non-tariff barriers on imported goods. The purpose is to protect domestic industries and retaliating against practices that are perceived as unfair (Adjemian et al. 2021). This strategy therefore aims at decreasing deficits of trade and promotes local productions; however, often disputes might establish global trade patterns. Contextually, it is to be said that tariffs would increase the costs of raw materials that are imported and intermediate goods. That is also by forcing the industries for reconfiguration supply chains and absorbing higher expenses regarding production.
Figure 1: New Tariffs Impact
(Source: weforum.org, 2025)
On the other hand, it is also to be stated that retaliatory measures by the targeted nations have compounded these effects by leading towards escalating protectionism cycle (Benguria et al. 2022). These types of policies however breed uncertainties, deterring FDI in long-term and creating distortions in the market. While being intended to shield markets domestically, these measures have frequently leading towards decreasing efficiency level alongside strained international relations. That has ultimately undermined national and global economic stability both throughout the interconnected networks of supply.
On the other hand, it can be stated that global supply chain would be representing intricate networks that would be moving raw materials, alongside intermediary components and finished products across the borders (Kim and Margalit, 2021). Certainly, in this accordance, it is to be considered that trade wars would be disrupting these networks through introduction of tariffs that can increase the cost of moving goods, while compelling companies for reconfiguration of production process and sourcing strategies. These adjustments however have often resulted into inefficiencies as well as delays that can compromise timelines of productions and holistic performance of the economies. Moreover, it can be evaluated that higher transportation and logistics costs would be coupled with unpredictable shifts in supply chain (Park et al. 2021). That is also by decreasing the benefits of international specialisation and economies of scale. In addition to this, it is also to be noted that prolonging uncertainties would be discouraging investments in context of innovation along with technologies. Thereby, it would be hampering improvements of productivity level. However, as companies are gradually adapting to these challenges, the ripple effects are observed to be extending beyond individual firms (Brutger et al. 2023). That is also by undermining economic efficiency in long-term and competitiveness in the highly competitive global marketplace.
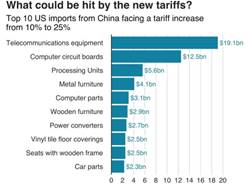
Significantly, in context of the current discussion of the article, exemplification of US-China Trade War can be given. This trade war has exemplified how tariffs that are escalated can create disruptions in the international markets (Fetzer and Schwarz, 2021). Thus, in this context, it can be seen that in the year 2018, United States had imposed tariffs on billions of dollars of imports from China, which had prompted China to be retaliating in similar manner. This specific escalation has further affected sectors like technology, agriculture and manufacturing.
Figure 2: Tariffs Escalation on US-China Bilateral Trade
(Source: weforum.org, 2025)
Moreover, American farmers are found to be suffering as access towards the Chinese markets have decreased, while on the other hand, Chinese manufacturers have incurred higher costs of production because of supply chain adjustments to be highly tariff-induced (Fajgelbaum et al. 2024). Certainly, in this accordance, it can be evaluated that the turning uncertainties have forced companies in revising strategies related to sourcing and diversification of supply chains, by altering trade patterns being long-established. Although specific domestic industries have seen benefits temporarily, holistic impacts had slowed the growth of the economy and increased the volatility in the market, while weakening confidence of the investors (Huang et al. 2023). This specific case therefore has highlighted the way protectionist measures regardless of its aim to support domestic industries would often create widespread uncertainties in the economy and disrupting global trade process and practices. Thus, it is serving as the cautionary statement for policymakers across the globe.
Moreover, in context of wider economic implications, it can be seen that trade wars would be extending their core impacts beyond individual industries. That would certainly influence broader global economy base. In addition to this, it is further to be stated that elevated tariffs would decrease volumes of international trade (Caliendo and Parro, 2022). Thereby, it might be dampening growth of the economies across the globe. Significantly, rising costs for the raw materials alongside finished goods would be rippling throughout the networks of production, leading towards higher prices for consumers and decreased purchasing power.
Figure 3: Wider Implications of Trade War
(Source: weforum.org, 2025)
Thus, with the mounting uncertainties, business investments would decline and confidence of the consumers would be eroding, which would ultimately slow the momentum of economy. Likewise; trade conflicts are also found to be straining diplomatic relations while fostering environment surrounding geopolitical tensions and instabilities (Ogunjobi et al. 2023). This uncertainty would discourage investments in long-term, specifically across the emerging markets and can equally disrupt the global financial markets.
In summary, it can be implied that trade wars would be having complex as well as might often have detrimental impacts on the global economic stance. They would be disrupting supply chains, elevating costs of production alongside discouraging investments. The exemplification of the US-China Trade War has exhibited how those conflicts could alter the dynamics of the market and forcing industries as well as the governments in adapting to new reality of rising uncertainties and shifting power of economy. Ultimately, on suggestive perspective, it can be stated that mitigating the adverse impacts of trade wars would certainly require balanced approach that would be considering national interests as well as global integration of economies both simultaneously. This balance is certain critical to foster sustainable growth and ensuring globalisation and its benefits to continually be shared vastly throughout the nations.
Adjemian, M.K., Smith, A. and He, W., 2021. Estimating the market effect of a trade war: The case of soybean tariffs. Food Policy, 105, p.102152.
Benguria, F., Choi, J., Swenson, D.L. and Xu, M.J., 2022. Anxiety or pain? The impact of tariffs and uncertainty on Chinese firms in the trade war. Journal of International Economics, 137, p.103608.
Brutger, R., Chaudoin, S. and Kagan, M., 2023. Trade wars and election interference. The review of international organizations, 18(1), pp.1-25.
Caliendo, L. and Parro, F., 2022. Trade policy. Handbook of international economics, 5, pp.219-295.
Fajgelbaum, P., Goldberg, P., Kennedy, P., Khandelwal, A. and Taglioni, D., 2024. The US-China trade war and global reallocations. American Economic Review: Insights, 6(2), pp.295-312.
Fetzer, T. and Schwarz, C., 2021. Tariffs and politics: evidence from Trump’s trade wars. The Economic Journal, 131(636), pp.1717-1741.
Huang, H., Ali, S. and Solangi, Y.A., 2023. Analysis of the impact of economic policy uncertainty on environmental sustainability in developed and developing economies. Sustainability, 15(7), p.5860.
Kim, S.E. and Margalit, Y., 2021. Tariffs as electoral weapons: The political geography of the US–China trade war. International organization, 75(1), pp.1-38.
Ogunjobi, O.A., Eyo-Udo, N.L., Egbokhaebho, B.A., Daraojimba, C., Ikwue, U. and Banso, A.A., 2023. Analyzing historical trade dynamics and contemporary impacts of emerging materials technologies on international exchange and us strategy. Engineering Science & Technology Journal, 4(3), pp.101-119.
Park, C.Y., Petri, P.A. and Plummer, M.G., 2021. The economics of conflict and cooperation in the Asia-pacific: RCEP, CPTPP and the US-China trade war. East Asian economic review, 25(3), pp.233-272.
weforum.org, (2025), This is how much the US-China trade war could cost the world, according to new research, Available at: https://www.weforum.org/stories/2019/06/this-is-how-much-the-us-china-trade-war-could-cost-the-world-according-to-new-research/ [Accessed on 07.02.2025]
academhelper.com academhelper.com
"Looking for a Similar Assignment? Get Expert Help at an Amazing Discount!"